How does DNS work?
When you type an address into your browser and press return there are those couple of seconds where your computer has a think before it starts to download the web page you are looking for. It is in these couple of seconds where DNS comes in to play. Let’s use an example to explain this.
If you type in a web address such as https://admin.names.co.uk and your computer doesn’t know where to find the web page, it simply does what we would do…it asks.

But who does it ask?
Well with every internet provider there are servers that are called DNS resolvers. Your computer starts by asking these DNS resolvers ‘where is admin.names.co.uk?’ If the resolver knows it will simply respond with the location. Your computer will go to that location and, hey presto, the web page at admin.names.co.uk appears.
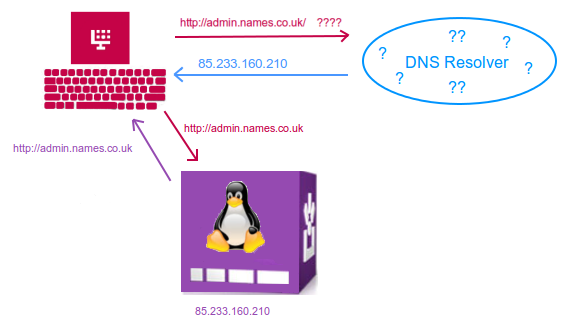
As you can see above, the computer asks the DNS resolver for the location of admin.names.co.uk, and the DNS resolver returns the answer of 85.233.160.210. Now your computer has the location (IP Address), it goes to the web server to retrieve the webpage.
But, what if the DNS resolvers do not know where to find admin.names.co.uk?
In this situation the DNS resolver will go looking for the answer…
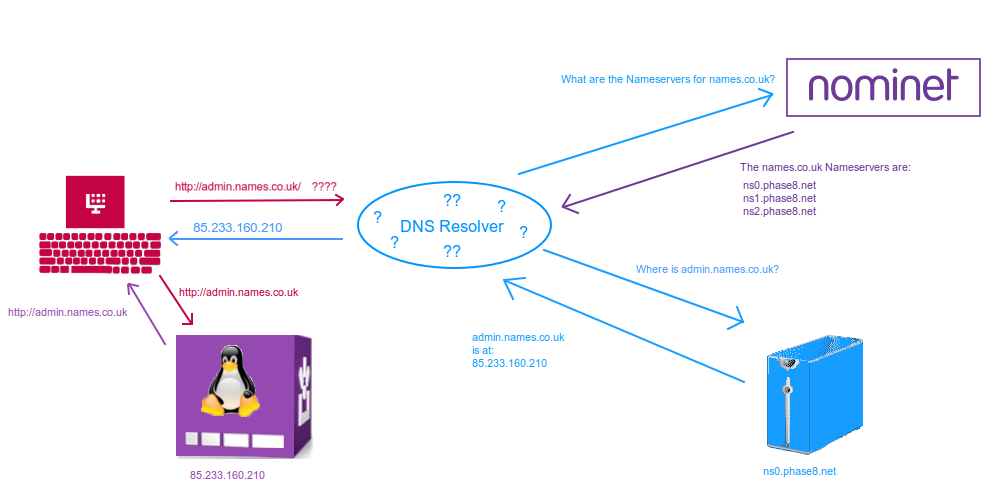
This may look complicated but we have split it into sections below.
As before, the computer asks the DNS resolver for the location of admin.names.co.uk, but as the DNS resolver does not know where names.co.uk is located, it has to find out.
The DNS resolver starts by reading the address from right to left, starting with .co.uk. As all .co.uk domains are managed through Nominet this will be the first stop.
The DNS resolver goes to Nominet and asks, What are the nameservers for names.co.uk?. (Nameservers are servers that store the DNS for a domain.) The Nominet servers will tell the DNS resolver what the nameservers are for names.co.uk.
In this case the nameservers for names.co.uk are ns0.phase8.net, ns1.phase8.net and ns2.phase8.net – these are the servers that store the DNS for names.co.uk.
With this new information the DNS resolver then asks ns0.phase8.net for the location of admin.names.co.uk.
The nameservers tell the DNS resolver that admin.names.co.uk is at 85.233.160.210, and the information is passed back to your computer. Your computer will go to that location, and once again the web page will appear.
After this, the DNS resolver will store the answer for 24 hours in case anyone else asks for that particular website.
All of this happens in a couple of seconds, and now that the DNS resolver has stored the information it has found, the website will appear even faster should we search for it again.